Introduction
Strings are nothing but sequence of characters.
We can store the strings in c using character arrays.
The last character in the character array is always ‘\0’
(null). It marks the end of the string.
Below are some of the different ways of storing the strings
in c.
Character arrays declaration
Syntax:
char str[number-of-characters];
char str1[] = "sagar";
char str2[3] = {'a','b','\0'};
char str3[6] = "sagar";
char* str4;
Declaration
of string
Example 1:
char name[15];
Initializing string
Example 2:
char name[15]="Sagar salunke";
Below program will calculate the length of the string.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char str[15];
int i=0;
printf("\n Enter
String : ");
scanf("%s",str);
while(str[i]!='\0')
{
i++;
}
printf("\n %s Length
is=%d\n",str,i);
getchar();
}
Below program will reverse the given string.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char str[15];
int i=0,j=0;
printf("\n Enter
String : ");
scanf("%s",str);
printf("\n String is
:%s\n",str);
while(str[i]!=NULL)
{
i++;
}
printf("Reverse
string is:");
for(j=i;j>=0;j--)
{
printf("%c",str[j]);
}
getchar();
}
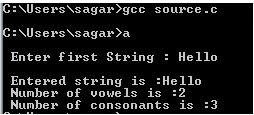
Below program will count the vowels and consonants
in the string.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char s1[15];
int i=0,c1=0,c2=0;
printf("\n Enter
first String : ");
scanf("%s",s1);
while(s1[i]!='\0')
{
if(s1[i]=='a'||s1[i]=='e'||s1[i]=='i'||s1[i]=='o'||s1[i]=='u')
{
c1++;
}
else
{
c2++;
}
i++;
}
printf("\n Entered
string is :%s",s1);
printf("\n Number of vowels is
:%d",c1);
printf("\n Number of consonants is
:%d",c2);
getchar();
}
Below program will convert the upper case string to
lower case.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char str[15];
int i=0;
printf("\n Enter
String : ");
scanf("%s",str);
printf("\n String is
:%s\n",str);
while(str[i]!='\0')
{
if(str[i]>=65
&& str[i]<=96)
{
str[i]=str[i]+32;
}
i++;
}
printf("Converted
string is:%s",str);
getchar();
}
Below
program will copy one string into another.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char s1[15],s2[15];
int i=0;
printf("\n Enter
first String : ");
scanf("%s",s1);
printf("\n Enter
second String : ");
scanf("%s",s2);
printf("\nBefore
copying:");
printf("\n First
string :%s \n Second string :%s",s1,s2);
for(i=0;i<=14;i++)
{
s2[i]=s1[i];
}
printf("\n After
copying:");
printf("\n First
string :%s \n Second string :%s",s1,s2);
getchar();
}









No comments:
Post a Comment
Leave your valuable feedback. Your thoughts do matter to us.